

Efficiency of a motor is a measure of how well it is capable of converting electrical energy into mechanical work. Lost energy is emitted in the form of heat.
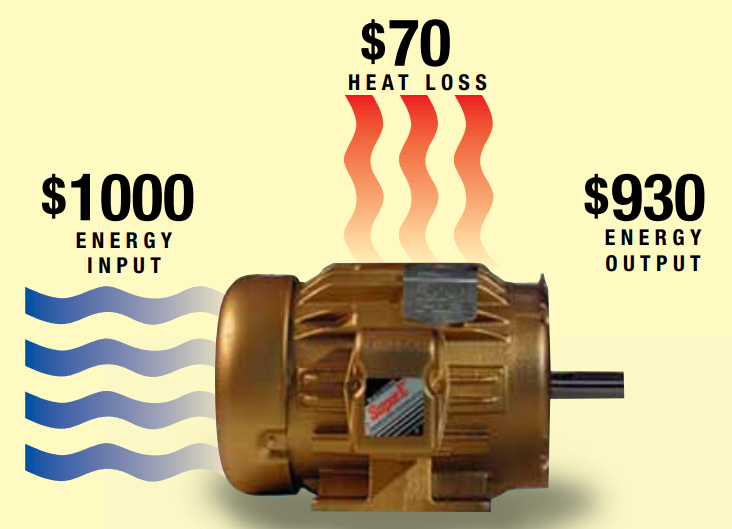
Efficiency is ratio between mechanical output and electrical input. High efficiency means that the motor is converting electrical power to mechanical power with small losses.
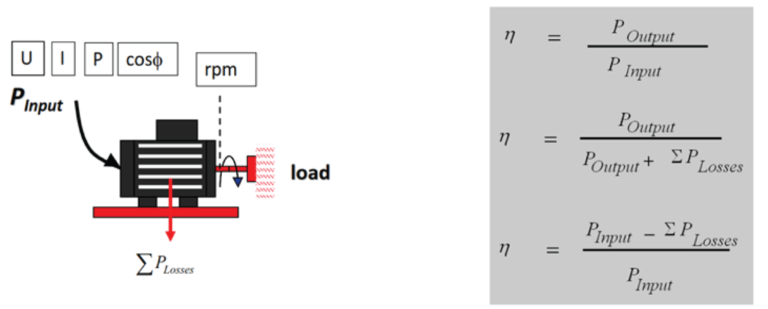
To increase efficiency, losses have to be reduced. Motor losses can be divided into five main categories. The first category is iron losses in the core, the second windage and friction losses. Load losses, which vary with the load, are classified into copper losses in the stator, rotor losses, and stray load losses. All losses can be influenced by motor design and construction solutions.
To increase efficiency, losses have to be reduced. Motor losses can be divided into five main categories. The first category is iron losses in the core, the second windage and friction losses. Load losses, which vary with the load, are classified into copper losses in the stator, rotor losses, and stray load losses. All losses can be influenced by motor design and construction solutions.

Iron losses in the core are caused by the energy required to overcome the opposition to changing magnetic fields in the core material. These losses can be reduced by using better-quality steel and by lengthening the core to reduce magnetic flux density. Windage and friction losses are caused by air resistance and bearing friction. Improved bearing design and bearing seal selection, air flow and fan design affect these losses. The fan must be large enough to provide adequate cooling, but not so large as to reduce efficiency and increase noise. To reach an optimal cooling effect in each motor, blade sizes and pitches vary in different fan models.
Load losses, stator copper losses (also referred to as I2R losses) are caused by heating from the current flow through the resistance of the stator winding. Techniques for reducing these losses include optimizing the stator slot design. Rotor losses are depending on the slip. These losses are reduced for example by increasing the size of the conductive bars and end rings to produce lower resistance. Stray load losses are the result of leakage fluxes induced by load currents. These can be decreased by improving slot geometry. Completely new motor designs are also developed to increase efficiency beyond known limits.