

An AC motor has due to its construction a starting current of app. 3.5-7 time the nominal current. This phenomena often causes problems.
•In the supply network such as:
• voltage drop
• high transients
•and in some cases uncontrolled shutdown
• As great mechanical stress on the motor.
• Rotor bars
• stator windings
• For driven equipments, processes, and the foundation is affected by starting of an AC electrical motor
The choice of starting method depends on:
• Permitted starting current
• Short circuit capacity on the network
• Maximum allowed voltage drop on the terminals during start
• Minimum starting torque
• Load inertia
• Process requirements
• Economic aspect
• There has been developed several starting methods where the basic goal has been to reduce the starting current and then the voltage drop
• Partly the same starting equipment is used when starting constant speed induction motors and constant speed synchronous motors as synchronous motors are normally started as induction motors
• Direct on line starting ( DOL)
• Star Delta Starting
• Soft Staters
• Reactor starting
• Capacitor starting
• Reactor / Capacitor starting
• Autotransformer starting
• Frequency-controlled starting
• Starting resistors for Slip-ring motors
• Pony motor starting
• Hydraulic coupling
• Other
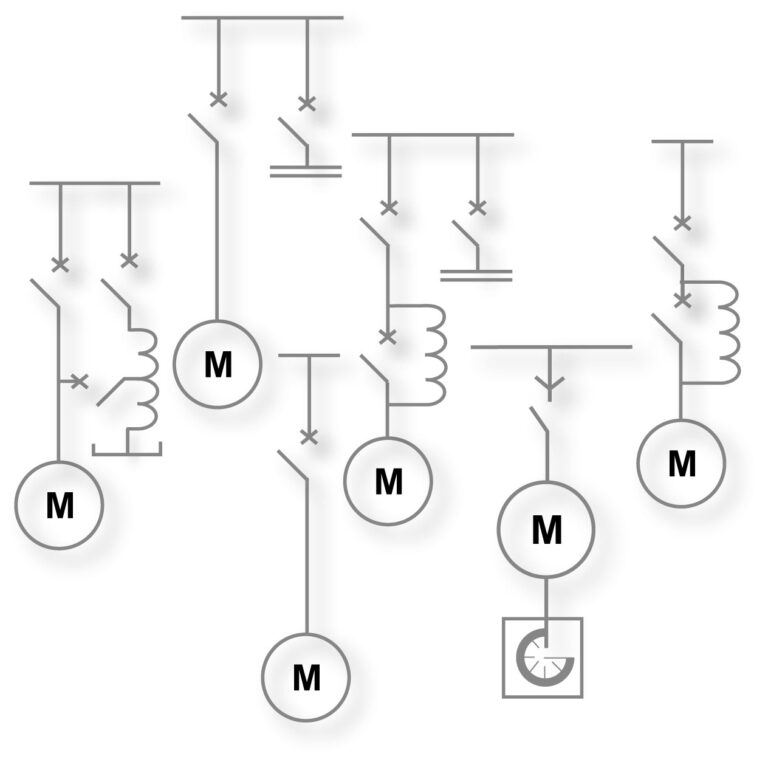
Here we see some of the starting methods used in present days
• Require that the network is infinite
• In real will the voltage drop and we must consider that in the motor design
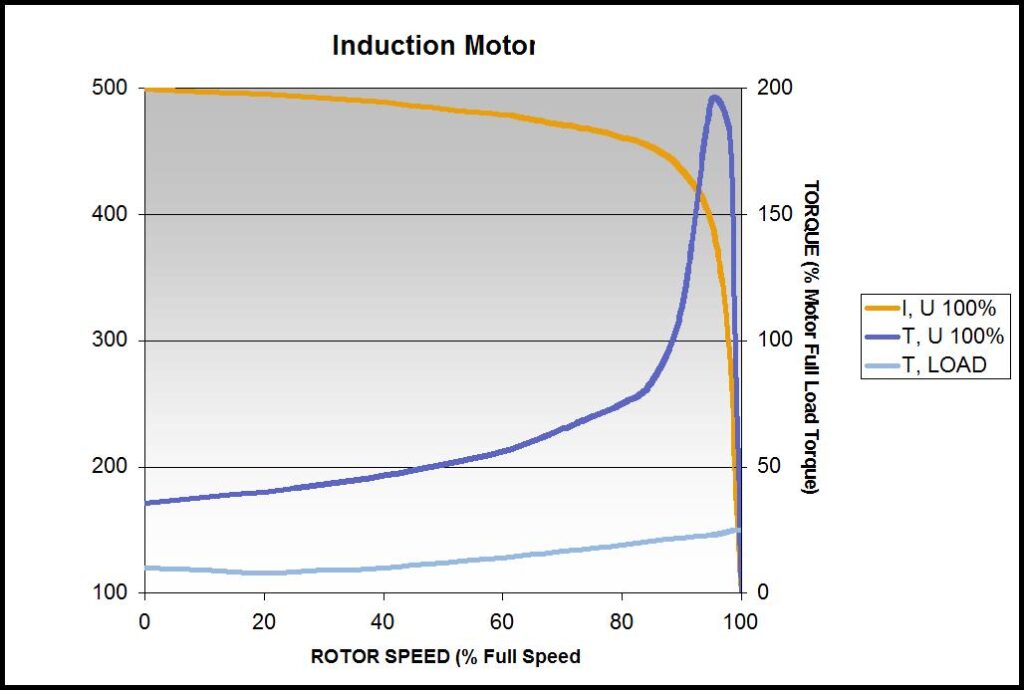


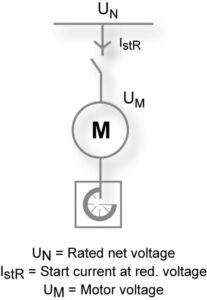
• For strong networks DOL is the most common starting method
• Suitable for stable supplies and mechanically stiff and well dimensioned shaft systems
• Limited starting current by motor design for DOL
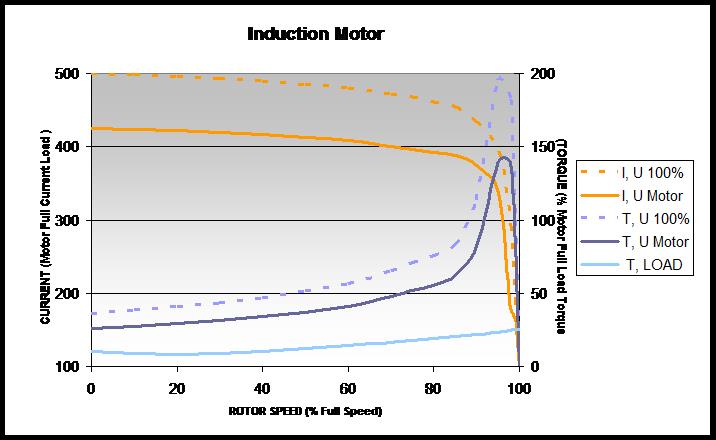
If it is necessary to restrict the starting current of a motor because of supply limitations, the star-delta (Y/Δ) method can be employed. When a motor wound for 400 V/Δ, for instance, is started with winding Y connected, this method will reduce the starting current to about 30 per cent of the current reached with DOL, and the starting torque will be reduced to about 25 per cent of its DOL value.
However, before using this method, it must be determined whether the reduced motor torque is sufficient to accelerate the load over the motor’s speed range.
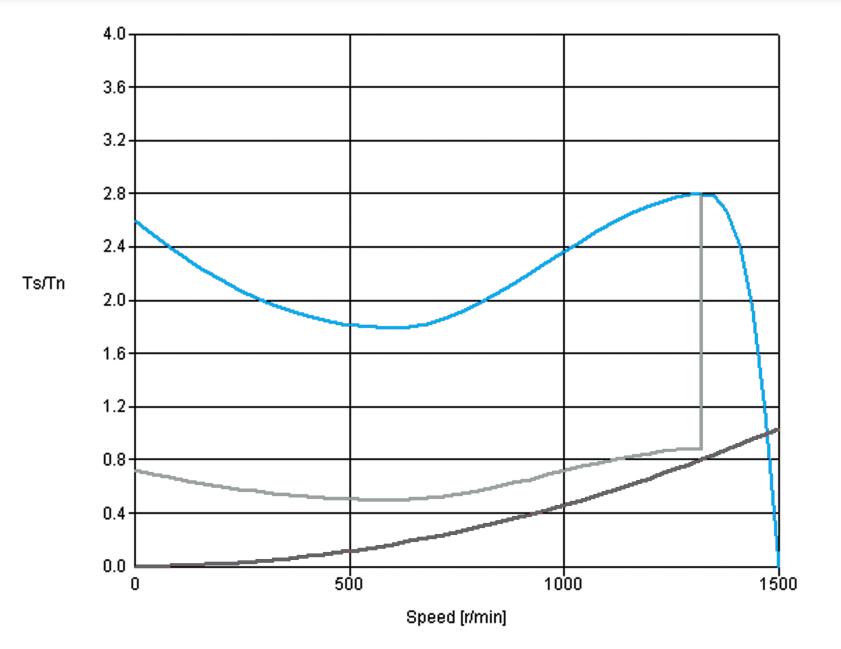
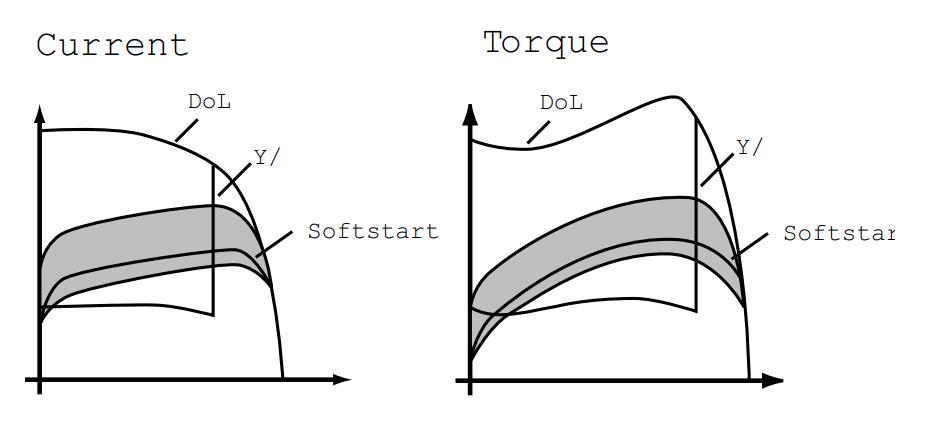
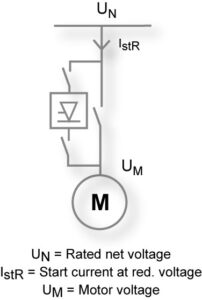
A soft starter limits the starting current of the motor and so provides a smooth start. The magnitude of the starting current is directly dependent on the static torque requirement during a start and on the mass of the load to be accelerated.
The starting principle of a soft-starter is based on a fast-acting semiconductor, called a thyristor. It is also known as silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) that can have four terminals.
The starting voltage of an electric motor is reduced depending on the angle of conduction of the thyristors, thus decreasing the peaks in the current, one of the duties of a soft-starter is to control the power of a motor without changing its frequency.
Some soft starters have adjustable settings to meet any application requirements. Gradually increasing the motor voltage, and thereby torque, results in a very smooth start. When the motor is well up in speed, it is common to bypass the soft starter to avoid power loss from the semiconductors during continuous operation
•The principle of a frequency-controlled starting is that it take place at low frequency, resulting in a low speed which is then run up to operating speed by increasing the frequency
•The frequency converter enables low starting current because the motor can produce rated torque at rated current in practice from zero to full speed
•Variable frequency start (VSD start) gives full torque from 0 rpm without voltage drop
• On a slip ring motor one can increase the rotor circuits resistance with an external resistance
• This method is usually chosen when the supply network is weak and the required starting torque and moment of inertia are very high
• By switching in the additional resistances in steps (normally 4-7) the desired acceleration torque can be obtained
• After the motor has reached its rated speed the rotor winding is short-circuited and the motor runs as a normal cage induction motor
| Sr. No. | Starting method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1 | Capacitor | Capacitor Strengthening the network. Requires more space to accommodate capacitor and breaker. Capacitor may cause high voltages. | Requires more space to accommodate capacitor and breaker. Capacitor may cause high voltages. |
| 2 | Autotransformer | Low starting current. Decrease in starting torque only proportional to current. | More expensive than reactor starting. |
| 3 | Frequency-controlled starting | Motor in synchronism throughout starting process. No torque limitations. For all applications. | Frequency-controlled starting Motor in synchronism throughout starting process. No torque limitations. For all applications. Expensive equipment. |
| 4 | Reactor starting | Reactor starting Low starting current Extra reactor with breaker. Starting torque decrease proportional to square of starting current. | Extra reactor with breaker. Starting torque decrease proportional to square of starting current. |
| 5 | Reactor starting with capacitor | Same as reactor starting but with capacitor strengthening the network. | Same as reactor starting but requires more space to accommodate capacitor and breaker. Capacitor may cause high voltages. |
| 6 | D.O.L | Simple,no extra equipment required,high starting torque. | D.O.L. Simple, no extra equipment required. High starting torque. High starting current and high shaft stresses. Voltage drop may exceed what is acceptable. |
| 7 | Soft Starter | Soft Starter It is a smooth acceleration of full speed It is easy to operation, It is suitable for all types of induction motors. More expensive than other normal type of starter. In soft starter technology as compared to the frequency converter is that it is unable to control speed and it is also unsuitable for applications requiring speed control | More expensive than other normal type of starter. In soft starter technology as compared to the frequency converter is that it is unable to control speed and it is also unsuitable for applications requiring speed control |
| 8 | Star Delta The cheapest method to start a motor. The starting current is reduced to 33% of direct online starting current. Due to current reduction, torque is also reduced to 1/3 of direct online starting torque. More cable is required. | The cheapest method to start a motor. The starting current is reduced to 33% of direct online starting current. | Star Delta The cheapest method to start a motor. The starting current is reduced to 33% of direct online starting current. Due to current reduction, torque is also reduced to 1/3 of direct online starting torque. More cable is required. |