

Variable torque, constant torque and constant power are three basic load types for motor-driven systems. Pls see below common applications for which VFD may be considered and associated energy considerations for each of these load types.
| Motor Load Type | Load Curve | Common Applications | Pictures | Energy Considerations | |
| 1 |
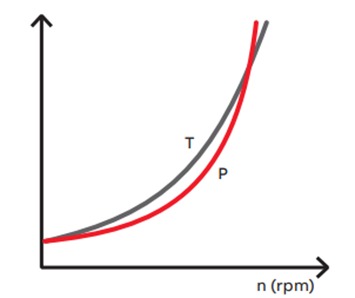
Variable Torque Load Power [hp] varies as the cube of the rotational speed Torque varies as the square of the rotational speed |
 |
|
|
Lower speed operation results in significant energy savings as shaft power of the motor drops with the cube of the rotational speed |
| 2 |
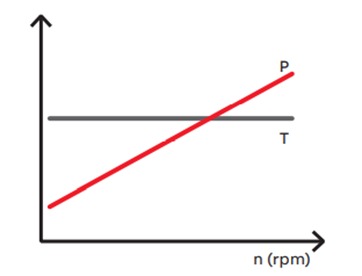
Constant Torque Load Torque remains constant at all rotational speeds Power [hp] varies directly proportional with rotational speed |
 |
|

|
Lower speed operation saves energy in direct proportion to the rotational speed reduction |
| 3 |
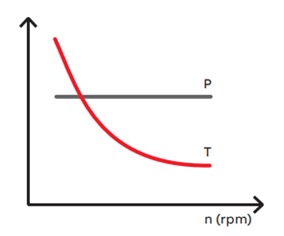
Constant Power [hp] Load Develops the same power [hp] at all rotational speeds Torque varies inversely proportional with the speed |
 |
|

|
No energy savings at reduced speeds; however, energy savings can be realized by attaining the optimized cutting and machining speeds for the part being produced; a time limiting switch device controlling no load operating time saves energy, too |