Motor Driven System
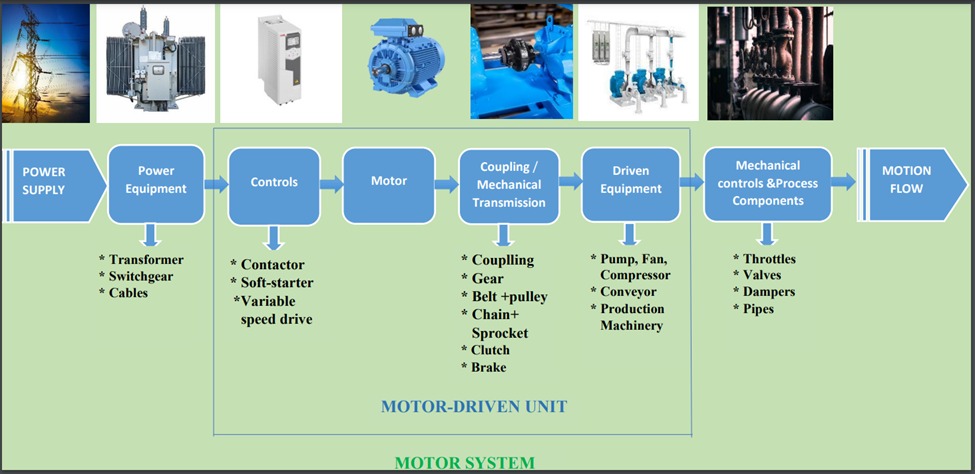
A motor is only one part of a “Machine System” that includes: Power in, the Motor and the Load.
Power Equipment:
The distribution transformer, which feeds the low-voltage bus, switchgear, meters, protection, command and control.
Controls: Soft Starter or Variable Speed Drive:
When the motor operates at a fixed speed, power is drawn directly from the main power supply. If a lot of power is needed to start a fixed-speed motor, an additional soft-start may be incorporated in the system. When the speed of the motor needs to vary, an electronic speed controller (alternatively known as a variable speed drive, variable frequency drive, inverter or converter) is used.
Mechanical Transmission:
The motor shaft may be coupled directly to the driven equipment through a coupling, a gearbox, a belt and pulley, or a chain and sprocket arrangement. There could additionally be an electromagnetic clutch for decoupling and a drum or disc brake for stopping quickly.
Driven Equipment:
This could be a water or an air pump, a fan, a gas compressor, a conveyor to move materials, or some type of production machine
Mechanical Controls and Process Components:
The remainder of the process can include pipes to carry liquids or gases, and valves, throttles and dampers to control the flow of liquids or gases.